|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| config | ||
| example/rust_test | ||
| figures | ||
| interfaces | ||
| ipc | ||
| services/dbinder | ||
| test/resource | ||
| utils | ||
| .gitattributes | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| BUILD.gn | ||
| bundle.json | ||
| Cargo.toml | ||
| CODEOWNERS | ||
| config.gni | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README_zh.md | ||
| README.md | ||
communication_ipc
Introduction
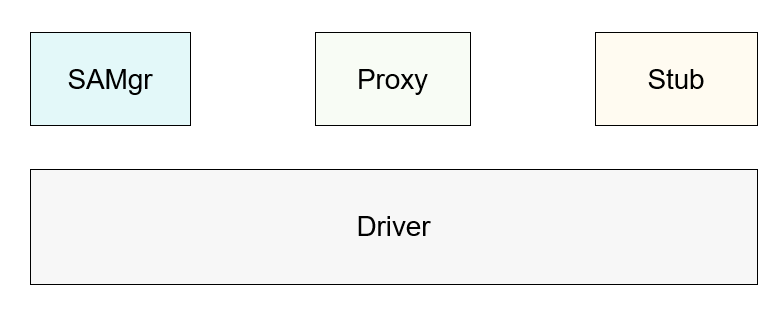
The inter-process communication IPC and remote procedure call RPC mechanisms are used to implement cross-process communication. The difference between them lies in that IPC uses the Binder driver to implement cross-process communication within a device, whereas RPC uses the DSoftBus driver to implement cross-process communication across devices. IPC and RPC generally use a client-server model. The service requester client can obtain the proxy of the service provider server and use the proxy to read and write data, thus implementing data communication between processes. Generally, the server registers system abilities SAs with the system ability manager SAMgr, which manages the SAs and provides APIs for the client. To communicate with a specific SA, the client must obtain the proxy of the SA from SAMgr. In this document, Proxy represents the service requester, and Stub represents the service provider.
Architecture
Directory Structure
/foundation/communication/ipc
├── interfaces # APIs exposed externally
│ └── innerkits # Header files for internal subsystems
│ ├── ipc_core # IPC APIs
│ └── libdbinder # dbinder APIs
├── ipc # IPC framework
│ ├── native # IPC native implementation
│ ├── src # IPC native source code
│ └── test # IPC native unit test cases
│ └── test # IPC native module test cases
├── service # dbinder implementation
│ └── dbinder # dbinder source code
Constraints
Currently, cross-device RPC communication is not supported.
Compilation and Building
Native Dependency
SDK dependency:
external_deps = [
"ipc:ipc_core",
]
In addition, the refbase implementation on which IPC/RPC depends is stored in //utils. Add the dependency on the Utils source code.
deps = [
"//utils/native/base:utils",
]
Usage
The procedure for implementing cross-process communication using native APIs is similar to that using Java APIs.
-
Define an interface.
The interface inherits IRemoteBroker and defines descriptors, functions, and message code.
-
Implement the server provider
stub.The stub inherits IRemoteStub(Native) or RemoteObject(Java) as well as AsObject and OnRemoteRequest.
-
Implement the service requester
proxy.The proxy inherits IRemoteProxy(Native) or RemoteProxy(Java), encapsulates functions, and calls SendRequest to send requests to the stub.
-
Register an SA.
After the process where the service provider resides starts, apply for the unique SA ID and register the stub with SAMgr.
-
Obtain the SA.
-
Obtain the proxy from the SAMgr based on the SA ID and device ID, and implement cross-process communication with the stub through the proxy.
Available APIs
Table 1 Native IPC APIs
Usage Guidelines
Native
Define the IPC interface ITestAbility.
ITestAbility inherits the IPC base class IRemoteBroker and defines descriptors, functions, and message code. The functions need to be implemented on both the proxy and stub.
class ITestAbility : public IRemoteBroker {
public:
// DECLARE_INTERFACE_DESCRIPTOR is mandatory, and the input parameter is std::u16string.
DECLARE_INTERFACE_DESCRIPTOR(u"test.ITestAbility");
int TRANS_ID_PING_ABILITY = 1; // Define the message code.
virtual int TestPingAbility(const std::u16string &dummy) = 0; // Define functions.
};
Define and implement service provider TestAbilityStub.
This class is related to the IPC framework and needs to inherit IRemoteStub<ITestAbility>. You need to override OnRemoteRequest on the stub to receive requests from the proxy.
class TestAbilityStub : public IRemoteStub<ITestAbility> {
public:
virtual int OnRemoteRequest(uint32_t code, MessageParcel &data, MessageParcel &reply, MessageOption &option) override;
int TestPingAbility(const std::u16string &dummy) override;
};
int TestServiceStub::OnRemoteRequest(uint32_t code,
MessageParcel &data, MessageParcel &reply, MessageOption &option)
{
switch (code) {
case TRANS_ID_PING_ABILITY: {
std::u16string dummy = data.ReadString16();
int result = TestPingAbility(dummy);
reply.WriteInt32(result);
return 0;
}
default:
return IPCObjectStub::OnRemoteRequest(code, data, reply, option);
}
}
Define the TestAbility class that implements functions for the stub.
class TestAbility : public TestAbilityStub {
public:
int TestPingAbility(const std::u16string &dummy);
}
int TestAbility::TestPingAbility(const std::u16string &dummy) {
return 0;
}
Define and implement TestAbilityProxy.
This class is implemented on the proxy and inherits IRemoteProxy<ITestAbility>. You can call SendRequest to send a request to the stub and expose the capabilities provided by the stub.
class TestAbilityProxy : public IRemoteProxy<ITestAbility> {
public:
explicit TestAbilityProxy(const sptr<IRemoteObject> &impl);
int TestPingService(const std::u16string &dummy) override;
private:
static inline BrokerDelegator<TestAbilityProxy> delegator_; // Use the iface_cast macro.
}
TestAbilityProxy::TestAbilityProxy(const sptr<IRemoteObject> &impl)
: IRemoteProxy<ITestAbility>(impl)
{
}
int TestAbilityProxy::TestPingService(const std::u16string &dummy) {
MessageOption option;
MessageParcel dataParcel, replyParcel;
dataParcel.WriteString16(dummy);
int error = Remote()->SendRequest(TRANS_ID_PING_ABILITY, dataParcel, replyParcel, option);
int result = (error == ERR_NONE) ? replyParcel.ReadInt32() : -1;
return result;
}
Send a request synchronously or asynchronously.
The MessageOption parameter for the sendRequest() method can be set to TF_SYNC, TF_ASYNC, using the MessageOption constructor or void SetFlags(int flags). The default value is TF_SYNC.
int SendRequest(uint32_t code, MessageParcel &data,
MessageParcel &reply, MessageOption &option) override;
MessageOption option;
option.setFlags(option.TF_ASYNC);
Register and start an SA.
Call AddSystemAbility to register the TestAbilityStub instance of the SA with SystemAbilityManager. The registration parameters vary depending on whether the SystemAbilityManager resides on the same device as the SA.
// Register the TestAbilityStub instance with the SystemAbilityManager on the same device as the SA.
auto samgr = SystemAbilityManagerClient::GetInstance().GetSystemAbilityManager();
samgr->AddSystemAbility(said, new TestAbility());
// Register the TestAbilityStub instance with the SystemAbilityManager on a different device.
auto samgr = SystemAbilityManagerClient::GetInstance().GetSystemAbilityManager();
ISystemAbilityManager::SAExtraProp saExtra;
saExtra.isDistributed = true; // Set a distributed SA.
int result = samgr->AddSystemAbility(said, new TestAbility(), saExtra);
Obtain the SA.
Call the GetSystemAbility function of the SystemAbilityManager class to obtain the IRemoteObject for the SA, and create a TestAbilityProxy instance.
// Obtain the proxy of the SA registered on the local device.
sptr<ISystemAbilityManager> samgr = SystemAbilityManagerClient::GetInstance().GetSystemAbilityManager();
sptr<IRemoteObject> remoteObject = samgr->GetSystemAbility(said);
sptr<ITestAbility> testAbility = iface_cast<ITestAbility>(remoteObject); // Use the iface_cast macro to convert the proxy to a specific type.
// Obtain the proxies of the SAs registered with other devices.
sptr<ISystemAbilityManager> samgr = SystemAbilityManagerClient::GetInstance().GetSystemAbilityManager();
sptr<IRemoteObject> remoteObject = samgr->GetSystemAbility(sdid, deviceId); // deviceId identifies a device.
sptr<TestAbilityProxy> proxy(new TestAbilityProxy(remoteObject)); // Construct a proxy.
Repositories Involved
DSoftBus subsystem
communication_ipc