In two contexts I tested it only reduces total coverage. If you want strict set of syscalls, reset corpus. |
||
|---|---|---|
| config | ||
| cover | ||
| csource | ||
| executor | ||
| fileutil | ||
| host | ||
| ipc | ||
| prog | ||
| rpctype | ||
| sys | ||
| sysgen | ||
| syz-fuzzer | ||
| syz-manager | ||
| tools | ||
| vm | ||
| .clang-format | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| AUTHORS | ||
| CONTRIBUTORS | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| Makefile | ||
| README.md | ||
| structure.png | ||
syzkaller - linux syscall fuzzer
syzkaller is a distributed, unsupervised, coverage-guided Linux syscall fuzzer.
It is meant to be used with KASAN (CONFIG_KASAN=y),
KTSAN (CONFIG_KTSAN=y),
or [KUBSAN] (http://developerblog.redhat.com/2014/10/16/gcc-undefined-behavior-sanitizer-ubsan/) (patch).
Project mailing list: syzkaller@googlegroups.com.
List of found bugs.
This is work-in-progress, some things may not work yet.
Usage
Various components are needed to build and run syzkaller.
- C compiler with coverage support
- Linux kernel with coverage additions
- QEMU and disk image
- The syzkaller components
Setting each of these up is discussed in the following sections.
C Compiler
Syzkaller is a coverage-guided fuzzer and so needs the kernel to be built with coverage support. Therefore, a recent upstream version of GCC is needed. Coverage support is submitted to gcc in revision 231296. Sync past it and build fresh gcc.
Linux Kernel
As well as adding coverage support to the C compiler, the Linux kernel itself needs to be modified to:
- add support in the build system for the coverage options (under
CONFIG_KCOV) - add extra instrumentation on system call entry/exit (for a
CONFIG_KCOVbuild) - add code to track and report per-task coverage information.
This is all implemented in this coverage patch;
once the patch is applied, the kernel should be configured with CONFIG_KCOV plus CONFIG_KASAN
or CONFIG_KTSAN.
QEMU Setup
Syzkaller runs its fuzzer processes inside QEMU virtual machines, so a working QEMU system is needed – see QEMU docs for details.
In particular:
- The fuzzing processes communicate with the outside world, so the VM image needs to include networking support.
- The program files for the fuzzer processes are transmitted into the VM using SSH, so the VM image needs a running SSH server.
- The VM's SSH configuration should be set up to allow root access for the identity that is
included in the
syz-manager's configuration. In other words, you should be able to dossh -i $SSHID -p $PORT root@localhostwithout being prompted for a password (whereSSHIDis the SSH identification file andPORTis the port that are specified in thesyz-managerconfiguration file). - The kernel exports coverage information via a debugfs entry, so the VM image needs to mount
the debugfs filesystem at
/sys/kernel/debug.
TODO: Describe how to support other types of VM other than QEMU.
Syzkaller
The syzkaller tools are written in Go, so a Go compiler (>= 1.4) is needed
to build them. Build with make, which generates compiled binaries in the bin/ folder.
Configuration
The operation of the syzkaller syz-manager process is governed by a configuration file, passed at
invocation time with the -config option. This configuration can be based on the
syz-manager/example.cfg; the file is in JSON format with the
following keys in its top-level object:
http: URL that will display information about the runningsyz-managerprocess.workdir: Location of a working directory for thesyz-managerprocess. Outputs here include:<workdir>/instance-x: per VM instance temporary files<workdir>/crashes/crashN-T: crash output files<workdir>/corpus/*: corpus with interesting programs
syzkaller: Location of thesyzkallercheckout.vmlinux: Location of thevmlinuxfile that corresponds to the kernel being tested.type: Type of virtual machine to use, e.g.qemuorkvm.count: Number of VMs to run in parallel.procs: Number of parallel test processes in each VM (4 or 8 would be a reasonable number).leak: Detect memory leaks with kmemleak (very slow).kernel: Location of thebzImagefile for the kernel to be tested; this is passed as the-kerneloption toqemu-system-x86_64.cmdline: Additional command line options for the booting kernel, for exampleroot=/dev/sda1.image: Location of the disk image file for the QEMU instance; a copy of this file is passed as the-hdaoption toqemu-system-x86_64.sshkey: Location (on the host machine) of an SSH identity to use for communicating with the virtual machine.cpu: Number of CPUs to simulate in the VM (not currently used).mem: Amount of memory (in MiB) for the VM; this is passed as the-moption toqemu-system-x86_64.enable_syscalls: List of syscalls to test (optional).disable_syscalls: List of system calls that should be treated as disabled (optional).suppressions: List of regexps for known bugs.
Running syzkaller
Start the syz-manager process as:
./bin/syz-manager -config my.cfg
The -config command line option gives the location of the configuration file
described above.
The syz-manager process will wind up qemu virtual machines and start fuzzing in them.
It also reports some statistics on the HTTP address.
Process Structure
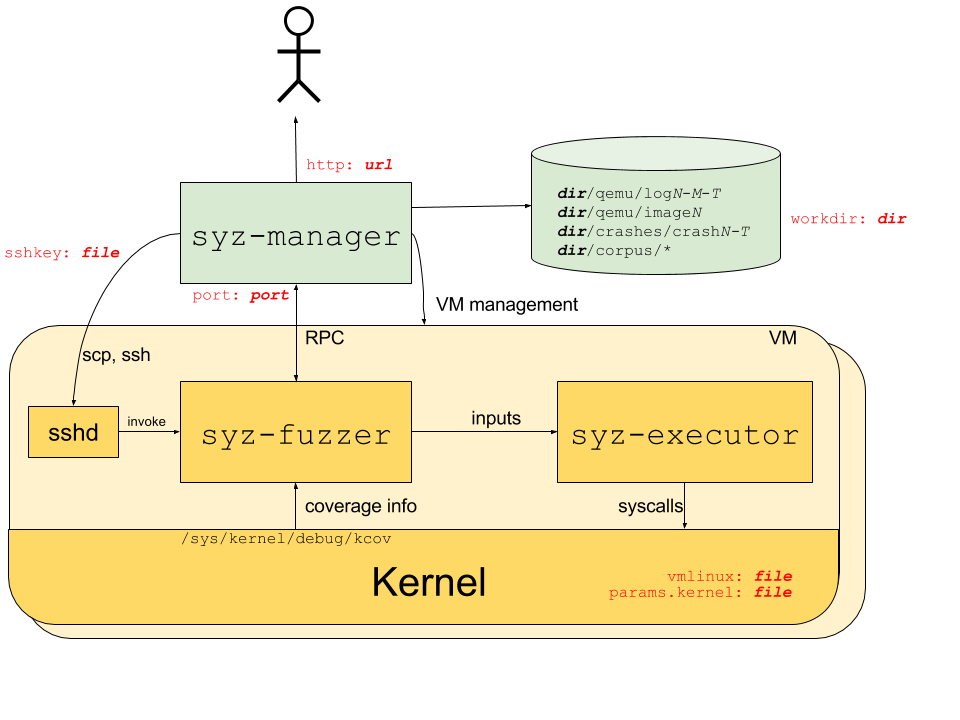
The process structure for the syzkaller system is shown in the following diagram; red labels indicate corresponding configuration options.
The syz-manager process starts, monitors and restarts several VM instances (support for
physical machines is not implemented yet), and starts a syz-fuzzer process inside of the VMs.
It is responsible for persistent corpus and crash storage. As opposed to syz-fuzzer processes,
it runs on a host with stable kernel which does not experience white-noise fuzzer load.
The syz-fuzzer process runs inside of presumably unstable VMs (or physical machines under test).
The syz-fuzzer guides fuzzing process itself (input generation, mutation, minimization, etc)
and sends inputs that trigger new coverage back to the syz-manager process via RPC.
It also starts transient syz-executor processes.
Each syz-executor process executes a single input (a sequence of syscalls).
It accepts the program to execute from the syz-fuzzer process and sends results back.
It is designed to be as simple as possible (to not interfere with fuzzing process),
written in C++, compiled as static binary and uses shared memory for communication.
Syscall description
syzkaller uses declarative description of syscalls to generate, mutate, minimize, serialize and deserialize programs (sequences of syscalls). Below you can see (hopefully self-explanatory) excerpt from the description:
open(file filename, flags flags[open_flags], mode flags[open_mode]) fd
read(fd fd, buf buffer[out], count len[buf]) len[buf]
close(fd fd)
open_mode = S_IRUSR, S_IWUSR, S_IXUSR, S_IRGRP, S_IWGRP, S_IXGRP, S_IROTH, S_IWOTH, S_IXOTH
The description is contained in sys/sys.txt file.
This is not an official Google product.