|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| benches | ||
| docs | ||
| examples | ||
| figures | ||
| src | ||
| tests | ||
| BUILD.gn | ||
| bundle.json | ||
| Cargo.toml | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| OAT.xml | ||
| README_zh.md | ||
| README.md | ||
| RELEASE_NOTE.md | ||
ylong_json
Introduction
ylong_json is a general JSON syntax parsing library that provides functions for converting JSON text to and from specific data structures.
ylong_json in OpenHarmony
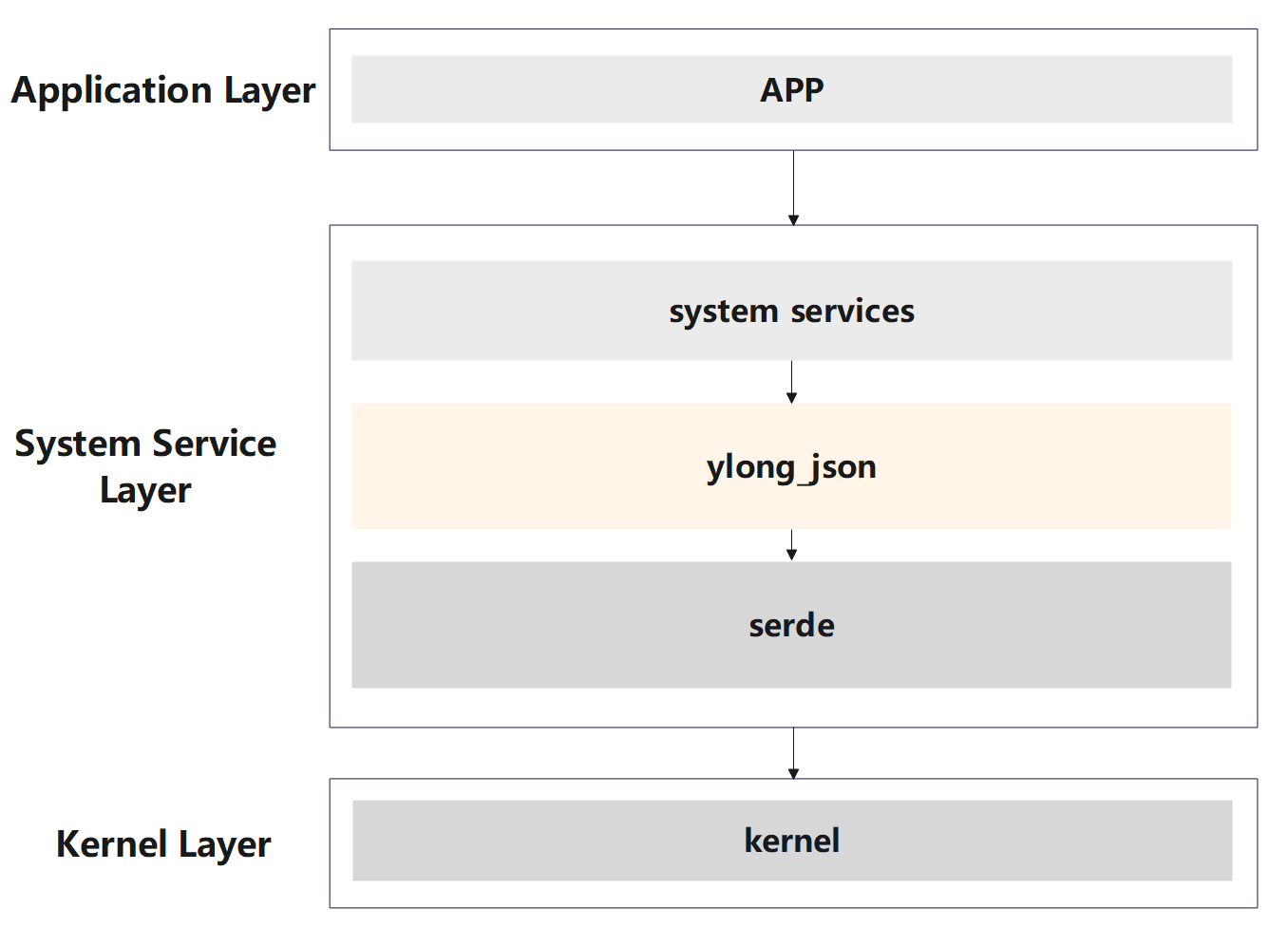 The following is a description of the key fields in the above figure:
The following is a description of the key fields in the above figure:
Application Layer: The application layer provides specific functions to users.App: Various applications need to use the functions of the system service layer.System Service Layer: System service layer, which provides system services to upper-layer applications.system services: Various system services require the use ofJSONrelated functions.ylong_json: System component, providing commonJSONserialization and deserialization capabilities to related components of the system service layer.serde: third-party library for efficient and versatile serialization and deserialization ofRustdata structures.
ylong_json Internal architecture diagram
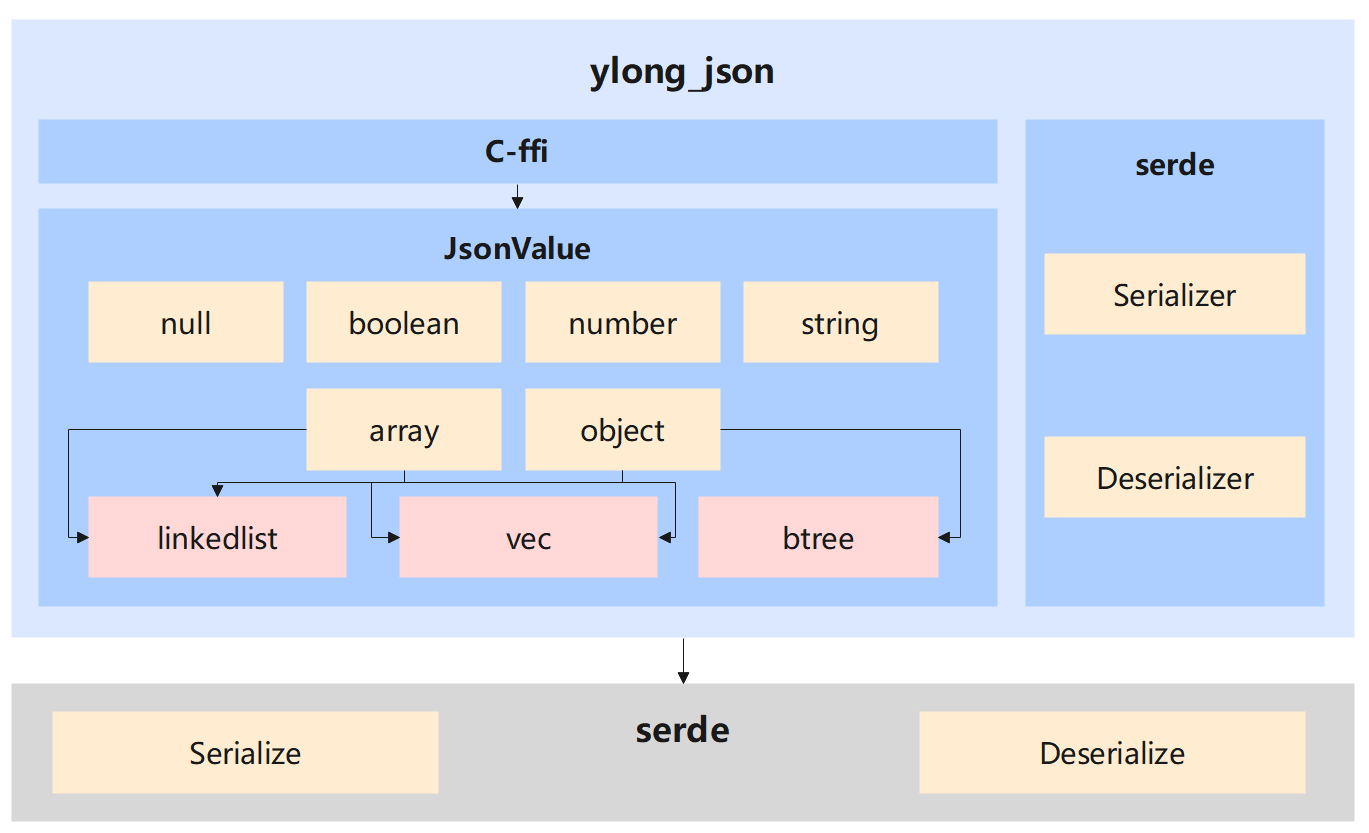
ylong_json is mainly divided into three submodules: JsonValue submodule, serde submodule, and C-ffi submodule.
The JsonValue submodule provides a basic data structure JsonValue.
JsonValue supports serializing itself into JSON text in either indented or compact format. Any syntactically correct JSON text can also be deserialized into a corresponding JsonValue data structure.
JsonValue supports addition, deletion, modification and query, and you can use the specified interface to change the data content in JsonValue.
JsonValue supports all data types in JSON syntax: null, boolean, number, string, array, object, and implements all its functions according to ECMA-404.
For array and object grammatical structures, JsonValue provides a variety of underlying data structures for different usage scenarios, for example, for array structures, it supports the underlying use of Vec or LinkedList, for object , supports the use of Vec, LinkedList or Btree as its underlying layer.
On different underlying data structures, array and object will reflect different creation and query performance, for example, object based on Btree data structure has higher performance in query, LinkedList or LinkedList or Vec has high performance in terms of creation.
The serde submodule provides procedural macro functions based on the Serialize and Deserialize traits provided by the serde third-party library, which can support fast conversion of user structures and JSON text.
The advantage of serde compared to JsonValue is that it is easy to use. Users do not need to convert the JSON text to JsonValue and then extract the specified data from it to generate the Rust structure. They only need to set Serialize' to the structure. and Deserialize process macro tags can be used to serialize the interface structure provided in ylong_json into JSON text, or convert the corresponding JSON text into a user structure.
The C-ffi module provides a C interface layer based on the JsonValue module, which facilitates users to use the C interface to call the functions of the ylong_json library.
Directory
ylong_json
├─ benches # Benche test files
├─ docs # Description documents
├─ examples # ylong_json code example
├─ figures # ylong_json structure charts
├─ src
│ ├─ value # Array and Object type definitions and related methods
│ ├─ adapter.rs # Adapts to the C interface implementation
│ ├─ consts.rs # Some definitions of constants and tables
│ ├─ deserializer.rs # Deserialization implementation of the adaptation serde
│ ├─ encoder.rs # Serialization implementation for the `JsonValue` type
│ ├─ error.rs # Error type definition, helpful to identify the problem
│ ├─ link_list.rs # LinkedList type definition and related methods
│ ├─ serializer_compact.rs # Serialization implementation of the adaptation serde
│ ├─ states.rs # Deserialization implementation for the `JsonValue` type
│ └─ value.rs # JsonValue type definition and related methods
└─ tests # Test directory
Build
Use Cargo
- Add
ylong_jsonto the dependency ofCargo.toml
[dependencies]
ylong_json = { git = "https://gitee.com/openharmony-sig/commonlibrary_rust_ylong_json.git" }
Use gn
- Add
ylong_jsoninbundle.json
“deps”: {
“components”: ["ylong_json"]
}
- Add
ylong_json:libinBUILD.gn
external_deps = ["ylong_json:lib"]
User Guide
See user_guide
Performance test
The following tests are from nativejson-benchmark。
The test environment information is as follows:
OS: Ubuntu 7.3.-16ubuntu3
Processor: Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6278C CPU @ 2.60GHz
CPU(s): 8
Memory:8.0 G
Software versions tested:
cJSON 1.7.16
Test Results:
======= ylong-json ==== parse | stringify ====
canada.json 200 MB/s 90 MB/s
citm_catalog.json 450 MB/s 300 MB/s
twitter.json 340 MB/s 520 MB/s
======== cJSON ======== parse | stringify ====
canada.json 55 MB/s 11 MB/s
citm_catalog.json 260 MB/s 170 MB/s
twitter.json 210 MB/s 210 MB/s
Description of test results:
Three test files are provided in the nativejson-benchmark test. Among them, canada.json contains a large number of number structures, the various data types of citm_catalog.json are relatively average, and twitter.json exists Various UTF-8 characters.
To ensure test fairness, ylong_json enables list_object, list_array and ascii_only feature.
The list_object and list_array features are mainly to ensure consistency with the cJSON data structure, and both are implemented using linked lists.
ascii_only feature is to ensure consistent processing logic for UTF-8 characters, cJSON does not handle UTF-8 characters.
The testing process is as follows:
- Read the content of the file into the memory, and get the content of the file
content. - Call the specified
JSONlibrary deserialization interface to generate the correspondingJSONstructuredata. - Call the serialization interface of the
JSONstructure to generate the output contentresult. - Using
content, loop deserialization generatesJSONstructure 100 times, taking the smallest processing timet1. - Using
data, serialize and generateJSONtext 100 times, taking the smallest processing timet2. - Calculate the parsing speed, the deserialization time is the length of
contentdivided byt1, and the serialization time is the length of theJSONtext divided byt2.